Home » Products » Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry » Elemental Analysis » Shimadzu Optical Emission Spectroscopy
High-Performance Spark Optical Emission Spectroscopy
For Metal Analysis
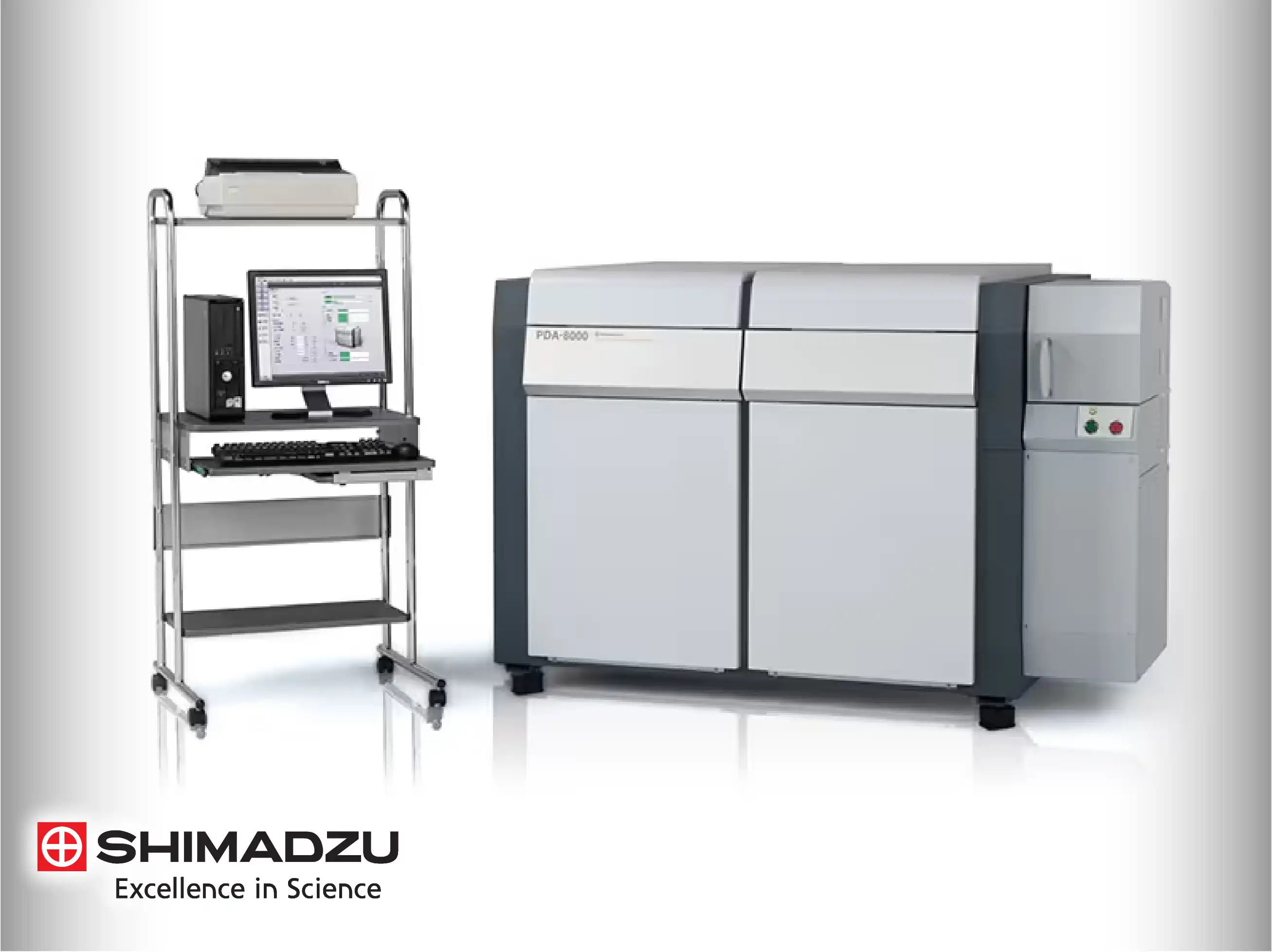
Shimadzu Optical Emission Spectroscopy
Shimadzu’s Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) philosophy focuses on the technical integration of high-speed hardware with "Analytical Intelligence" to streamline metal production workflows. Technically, the synergy between the digital spark generator and the vacuum-stabilized optical bench allows for the precise determination of critical elements like Nitrogen and Carbon in seconds.
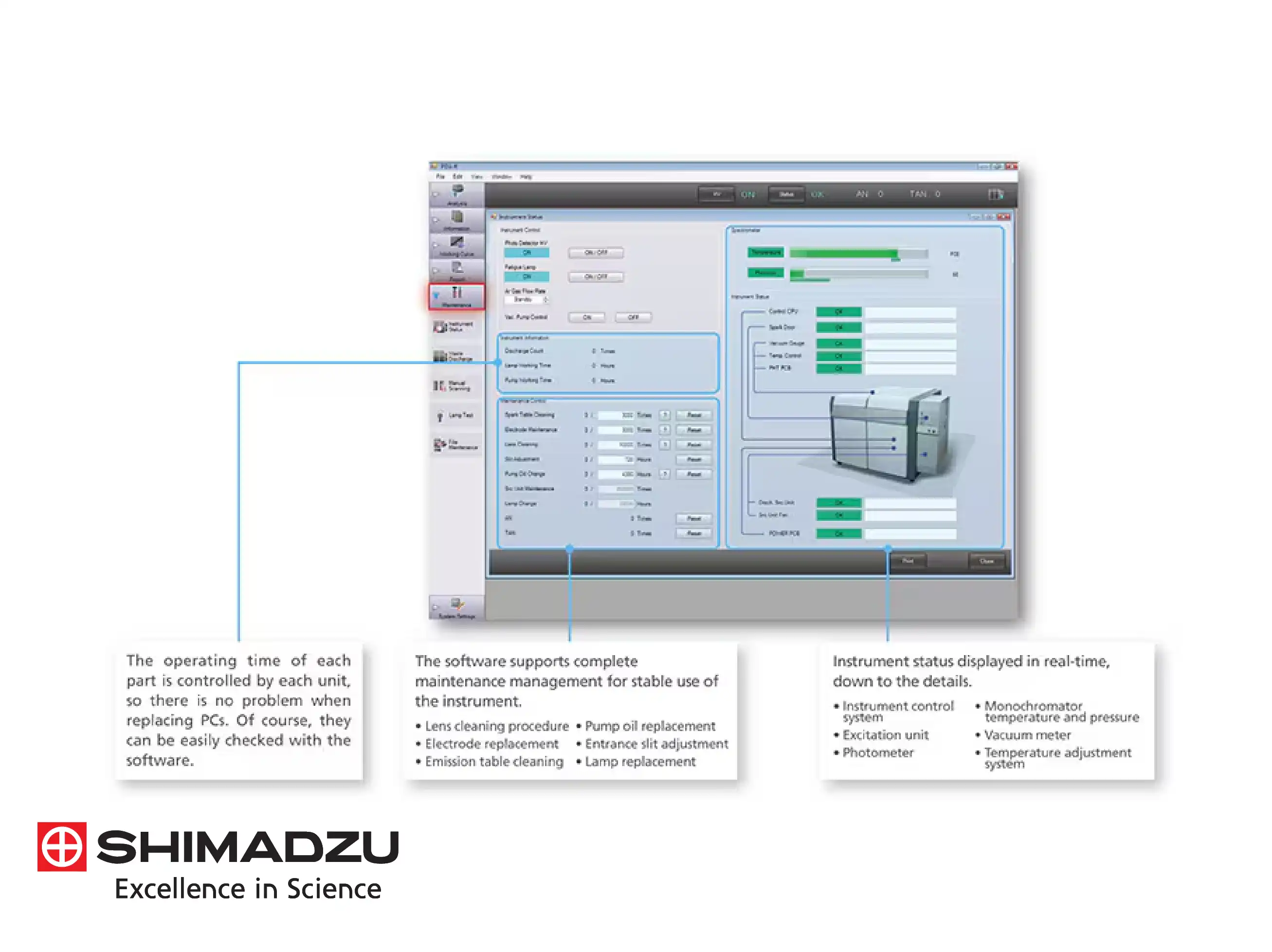
The software environment supports this by providing automated quality control checks and real-time diagnostic monitoring of gas pressures and vacuum levels. This integrated approach ensures that foundries and steel mills can maintain high-throughput operations with total data integrity, providing legally defensible results that are essential for verifying material certifications and ensuring the structural safety of metal components in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Fundamental Principles of Spark Discharge
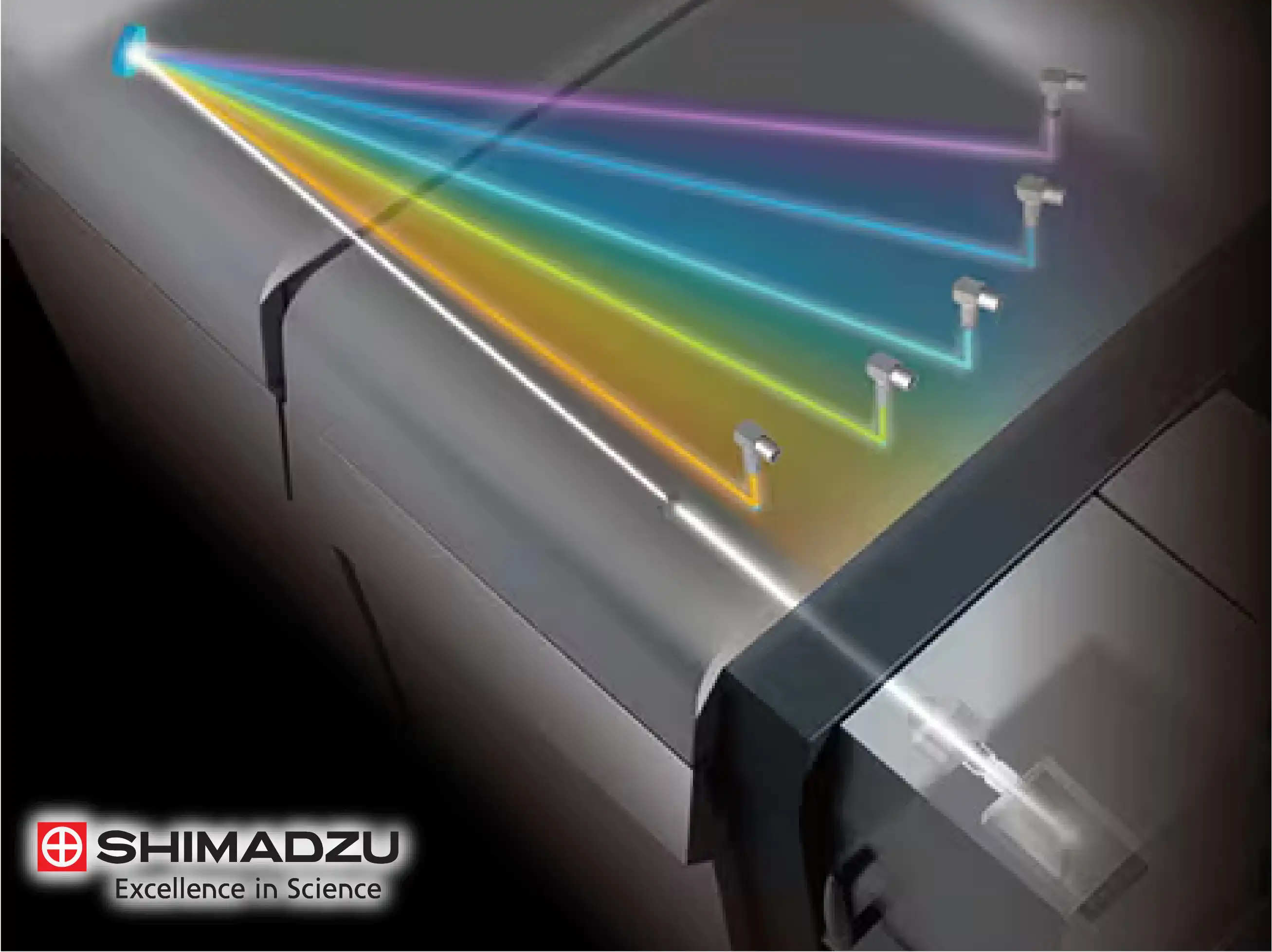
The technical foundation of Spark Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) lies in the generation of a high-frequency electrical discharge between an electrode and a metallic sample. Within an argon-purged spark stand, this discharge creates a localized plasma that vaporizes a minute portion of the material. Technically, this process excites the constituent atoms, which then emit light at wavelengths specific to their electronic structure, providing the raw data necessary for identifying the elemental composition of the alloy.
High-Resolution Rowland Circle Optics
To separate the complex light signals emitted by the spark, Shimadzu utilizes a high-resolution optical bench typically based on the Rowland circle configuration. Technically, this concave grating system ensures that light from the spark stand is focused with extreme precision onto a series of detectors. This arrangement allows for the simultaneous measurement of various wavelengths, enabling the instrument to quantify dozens of elements in a single spark sequence with minimal spectral overlap.
Vacuum Optics for Short-Wavelength Elements
A critical technical requirement for analyzing steel is the detection of elements like Carbon, Phosphorus, and Sulfur, which emit light in the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) range. Since oxygen absorbs these wavelengths, the optical chamber is maintained under a high vacuum. This vacuum-stable environment ensures that short-wavelength photons reach the detectors without attenuation, allowing for the precise determination of non-metallic elements that dictate the grade and quality of the metal.
Digital Pulse Distribution Control
Modern OES systems utilize digital pulse distribution control to manage the spark energy. Technically, this allows the system to vary the spark characteristics in real-time—from a high-energy "pre-spark" that homogenizes the sample surface to a stable "measurement spark" for data collection. This digital control improves the reproducibility of the discharge, leading to higher analytical precision and better detection limits across diverse matrices such as cast iron or aluminum alloys.
Time-Resolved Spectroscopy (TRS) Integration
Technically, Shimadzu incorporates Time-Resolved Spectroscopy (TRS) to enhance signal purity. By capturing the light emission at specific intervals within each spark pulse, the system can differentiate between the high-intensity background noise of the initial discharge and the characteristic elemental emission that follows. This filtering technique significantly improves the signal-to-noise ratio, enabling the detection of trace elements that would otherwise be obscured by the plasma background.
Automated Profile Alignment and Calibration
To maintain accuracy over long periods, the software includes automated profile alignment. Technically, thermal fluctuations can cause minor shifts in the light path; the system detects these shifts by measuring the position of a reference line and automatically adjusting the entrance slit or grating. This ensures that the light always hits the center of the detectors, maintaining calibration stability and reducing the frequency of manual re-standardization.
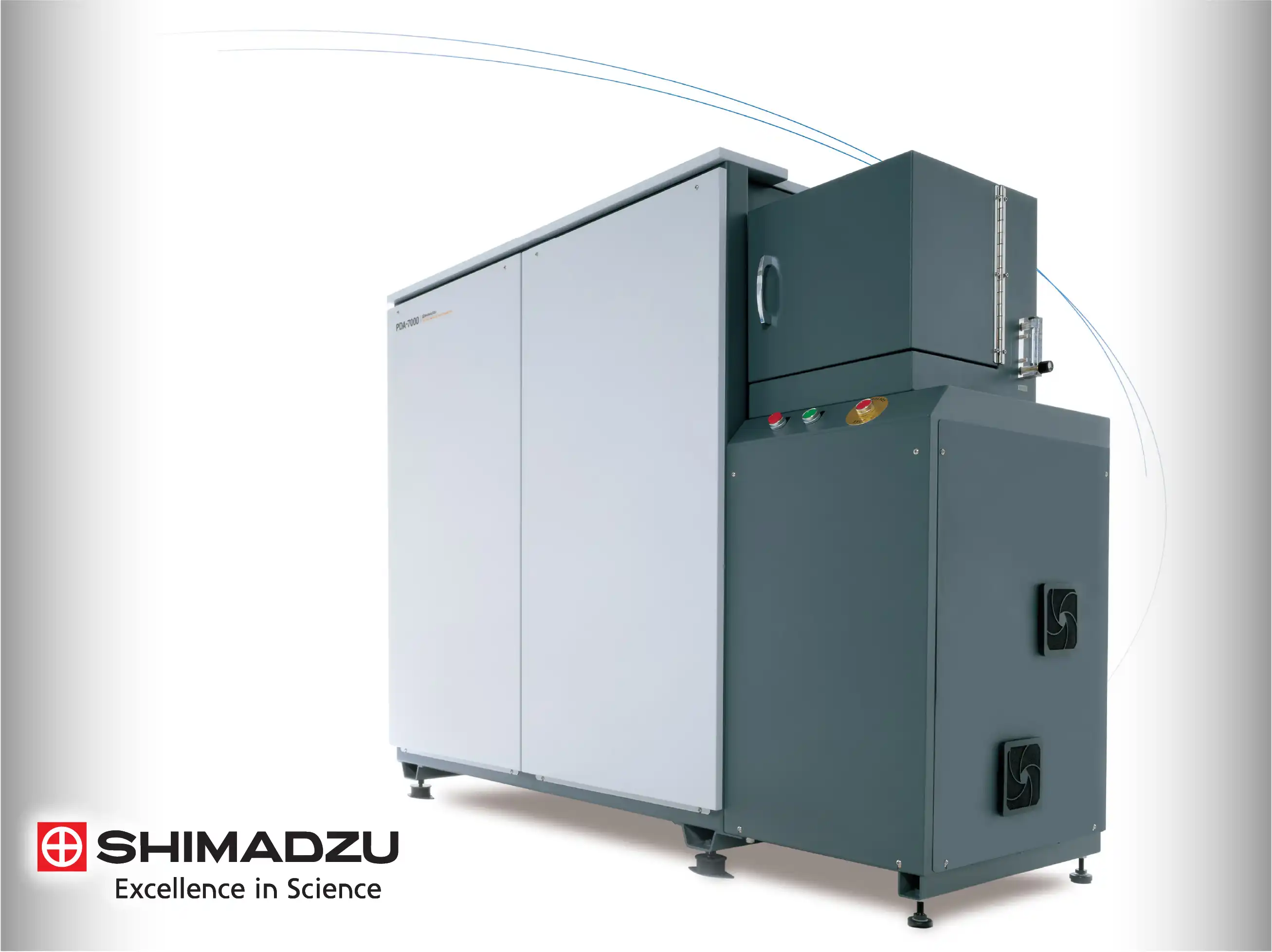
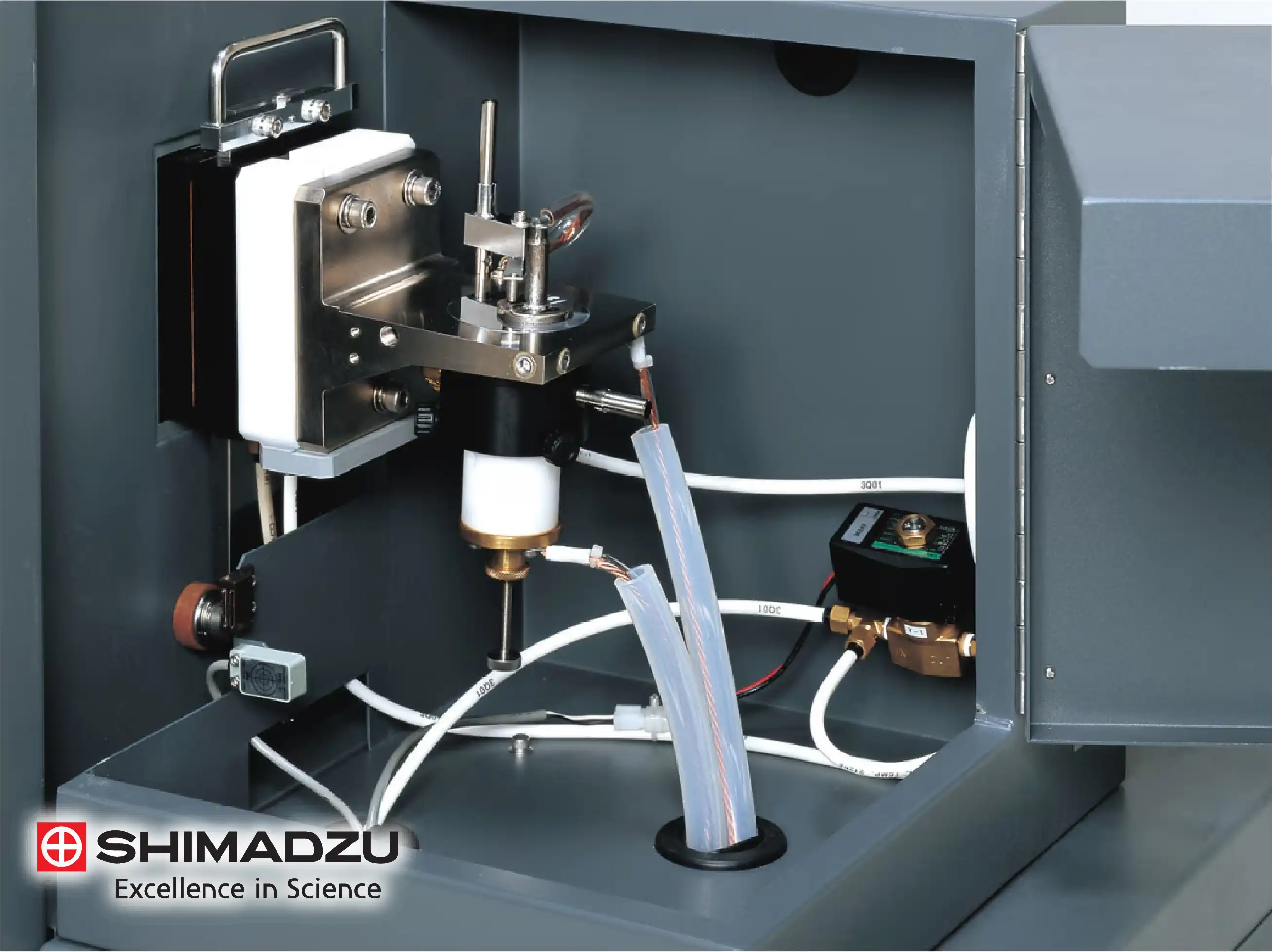
Argon Flow Optimization and Spark Stand Design
The design of the spark stand is technically optimized to ensure a stable argon atmosphere during the analysis. A precise flow of high-purity argon prevents atmospheric contamination, which would otherwise lead to erratic sparking and poor data quality. The stand is also engineered for easy maintenance, with a self-cleaning function that removes the metallic dust generated during vaporization, ensuring consistent electrical contact for every sample.
Integrated Data Management and Grade Identification
Beyond raw quantification, the software provides a technical framework for metal grade identification. By comparing the analyzed elemental concentrations against an integrated database of international standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN, JIS), the system can automatically identify the specific alloy grade. This real-time validation is essential in scrap metal recycling and foundry operations to prevent material mix-ups and ensure compliance with customer specifications.
Click here for more information about Shimadzu range of products
Related Products
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
Taawon for Laboratory & Scientific Supplies
Taawon Group © 2026 - All Rights Reserved
We use cookies to optimize site functionality and give you the best possible experience